หลังจากติดตั้งเสร็จแล้ว ก็มาดูส่วนการปรับแต่งในเวอร์ชั่นนี้ อาจจะอธิบายไม่หมดในหัวข้อนี้นะครับ
รายละเอียด (จะไม่มีในธีมตัวติดตั้งที่เป็น ออริจินอลทั่วไป)
– ใช้รูปแบบไอค่อนและการแสดงผลคล้าย Windows7 + การติดตั้งส่วนเสริมที่จำเป็นให้อัตโนมัติในขั้นตอนเดียว (รูปแบบธีมไม่ได้ใช้โปรแกรมแปลงโฉม TransFormation)
– มาตรฐานการทำงานบนโหมด AHCI ซึ่งมีใน Vista และ Windows7
– สะดวกและง่ายต่อการติดตั้งใช้งาน
– ค้นหาไดร์เวอร์หลักๆให้อัตโนมัติ (ติดตั้งเพิ่มเติมในส่วนอุปกรณ์เสริมต่างๆ)

** การใช้เมนู (ViStart) ในรุ่นนี้ ในช่อง Start Search ห้ามใช้พิมพ์คำสั่งในการเรียกโปรแกรม ให้ใช้ในเมนู RUN ตามเดิมนะครับ จะทำงานเพียงค้นหาเท่านั้น ไม่ได้ใช้รับคำสั่ง

การปรับค่าการใช้งาน ชุดเมนู (ViStart) สามารถยกเลิก/เรียกใช้ได้ กรณีพบปัญหาให้ยกเลิกใช้งานนะครับ ** แนะนำควรยกเลิกในหัวข้อ Start With Windows ในเมนู Option แล้วเริ่มระบบใหม่อีกครั้ง จะกลับไปใช้เมนูเดิมของ Windows Xp

แสดงการเรียกใช้ เมนู ผ่านการคลิ๊กขวาเมาส์ ในไอค่อน My Computer

การทำงานในตัวอย่างนี้ ทำงานบน ICH8 โหมด SATA2 AHCI ซึ่งเป็นรุ่นที่ออกมาขายนานพอสมควร รุ่นนี้ มี JmiCron SATA2 AHCI เพิ่มให้ใช้งานอีก 1 พอร์ต

แสดงเมนูแบบโปร่งใส *ใช้งานได้กับเมนูสไตล์ปกติ ไม่สามารถใชเแบบ Classic เมนูได้ ผู้ที่ต้องการใช้เมนูแบบ Classic ให้ยกเลิกก่อนครับ


การเรียกเมนูกลับคืน เมื่อเมนู Win7 ไม่ตอบสนองเมื่อคลิ๊กปุ่ม Start(ปุ่มเริ่ม)
Menu ในเวอร์ชั่นนี้ อาจพบปัญหาเมนูไม่ตอบสนอง ให้ตั้งค่ารูปแบบเมนูเป็นแบบคลาสสิคและเซ็ตกลับเป็นแบบเมนูมาตรฐาน การเรียกเมนูก็จะกลับมาดังเดิม (คลิ๊กขวาแถบงานขอบล่างจอภาพ เลือก Properties แล้วเลือกรูปแบบเมนู ตามที่กล่าวมา)

การเรียกใช้ Winroll เก็บหน้าต่างงานเหลือเพียงบาร์เท่านั้น กระทำได้โดย คลิ๊กขวาตรงบาร์ด้านบนของบานหน้าต่างๆนั้นๆ ส่วนการขยายกลับเพียงคลิ๊กขวาอีกครั้งก็จะกลับมาเต็มบานหน้าต่างเช่นเดิม

มุมมองพื้นหลังในโฟล์เดอร์ต่างๆ

การตั้งค่าปริ้นเตอร์ให้เป็นตัวเริ่มต้นในการพิมพ์ทุกโปรแกรม คลิ๊กขวาปริ้นเตอร์ตัวต้องการ เลือก Set as Default Printer

แสดงกล่องโต้ตอบเตือนความผิดพลาด ในการเข้าใช้งานระบบเครือข่าย/แชร์ไฟล์/เวิร์คกรุ๊ปได้ (ปกติค่าเริ่มต้นเป็นแบบนี้ ต้องเปิดการใช้งานแชร์ก่อน)

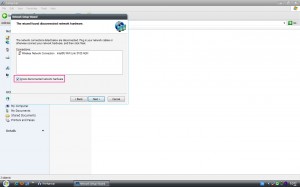
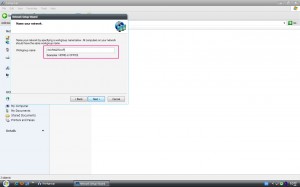
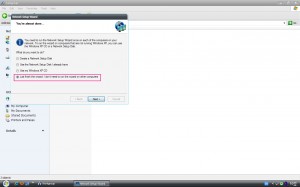
เริ่มต้นการเปิดใช้งาน แชร์ไฟล์ โดยใช้กล่องโต้ตอบของระบบ ซึ่งเป็นวิธีแนะนำ คลิ๊กผ่านบานหน้าต่าง My Network Places เลือกหัวข้อด้านซ้าย Setup a Home or Small Office Network จะแสดงบานหน้าต่าง Welcome To The Network Wizad

กรณีคลิ๊กขวาเปิดแชร์ไฟล์โดยตรง โดยไม่ทราบขั้นตอนการตั่งค่าอย่างถูกต้อง จะแสดงข้อความเตือนในบานหน้าต่างแชร์นั้นๆ

ข้อความในการแนะนำให้ตั้งค่าตามระบบมีให้เพื่อเปิดการใช้งานแชร์ไฟล์ คลิ๊ก If you understand the risks but still want to share the root of the drive click here

แสดงเนื้อหาการแชร์ข้อมูล ในหัวข้อ Network sharing and security จะแสดงข้อความแนะนำให้เรียกใช้ Network Setup Wizad ดังที่กล่าวมา กรณีไม่เรียกใช้ ผู้ใช้มีความชำนาญหรือแก้ไขปัญหาได้ คลิ๊ก If you understand the security risks but want to share files witout running the wizad click here

แสดงกล่องโต้ตอบเตือน การเรียกใช้ Network setup wizad แนะนำ ถ้าผู้ใช้สามารถแก้ปัญหาการทำงานที่ผิดพลาดที่จะเกิดขึ้นหลังจาการแชร์ไฟล์ ก็สามารถเลือก Just Enable file Sharing

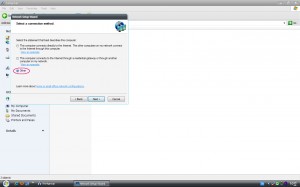
เริ่มเปิดใช้งานโดยเรียกใช้ Network Setup Wizad คลิ๊ก Next

คลิ๊ก Next ทำต่อไป กรณี มี 3 ตัวเลือก ให้เลือกในตัวเลือกกลาง คลิ๊ก Next

ตั่งค่าชื่อเครื่อง ตามสะดวก ควรเป็นชื่อที่ไม่ซ้ำกันในระบบและจดจำง่าย

ตั่งค่าตามเวิร์คกรุ๊ปที่ใช้ ควรเป็นกลุ่มเดียวกันเพื่อง่ายต่อการใช้งาน

คลิ๊กเลือกตัวเลือก Turn on file and printer sharing คลิ๊ก Next

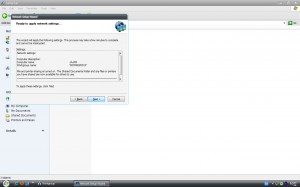
แสดงรายละเอียดการตั้งค่า

กำลังปรับการตั้งค่าที่ต้องการในระบบ

เลือกตัวเลือกล่างสุดในหน้านี้ คลิ๊ก Next

เสร็จสิ้นการตั้งค่าเปิดใช้งานแชร์ไฟล์ในเครือข่ายแล้ว คลิ๊ก Finish

ระบบจะแสดงการเริ่มระบบใหม่เพื่อโหลดค่าที่เปลี่ยนแปลงนี้ กรณีไม่แสดง แนะนำให้สั่งเริ่มระบบใหม่เองเพื่อลดความผิดพลาด

สามารถเข้าใช้งาน Workgroup ได้แล้ว





การเชื่อมต่อปริ้นเตอร์ในเครือข่าย เพื่อปริ้นข้ามเครื่องในเครือข่าย สามารถเข้าไปยังเครื่องที่มีการแชร์ไฟล์และปริ้นเตอร์ไว้ โดยผ่าน Network Place แล้วเข้าไปในเวิร์คกรุ๊ปหรือแฟ้มที่แสดงตามตำแหน่งที่ต้องการ กรณีเมื่อจะเชื่อมต่อปริ้นเตอร์ที่ต้องการ ให้คลิ๊กขวา เลือก Connect บนชื่อปริ้นเตอร์ตัวนั้น แล้วตอบ Yes ระบบจะทำการติดตั้งปริ้นเตอร์ตัวดังกล่าวไปยังเครื่องให้


การแชร์/ยกเลิกแชร์ปริ้นเตอร์


การดูชื่อเครื่องและเวิร์คกรุ๊ป

หน้า Network Connections

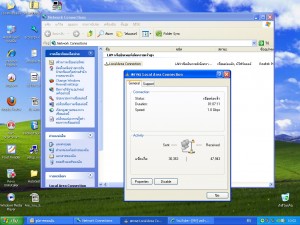
การเช็คสถานะการเชื่อมต่อของระบบแลนผ่าน LAN CARD/Wireless Lan


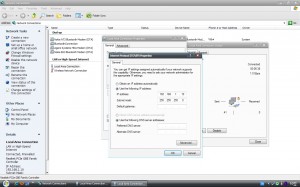
ดูคุณสมบัติของการเชื่อมต่อ Properties

การปรับแต่งการเชื่อมต่อแบบระบุหมายเลยเครื่องและเกตเวย์ (Manual Config)

ดูสถานะการเชื่อมต่อ


ชุดคำสั่งที่มีให้ใน Right Click

แสดงชุด Task Manager โดยเรียกจากการกดปุ่ม Ctrl+Alt+Delete พร้อมกัน
การปรับแต่ง อาการเข้าเกมแล้วภาพมัว เปิดโปรแกรมแล้วภาพมัว ที่เกิดจากการทำงานของชุดโปร่งใส ผ่านการกดแป้นคีย์ลัดโดยบังเอิญ
ตัวอย่างการเข้าเกม

การตั้งค่านี้สามารถนำไปใช้ได้กับทุกเครื่องที่ทำงานโปร่งใส

คลิ๊กขวา ไอค่อน Glass2K เลือก Setting

แสดงค่าปัจจุบัน

ตั้งค่า Trasparency Popup Right Click : Enabled

Keyboard Shortcuts : Disabled (เพื่อยกเลิกปุ่มลัดที่อาจกดตรงระหว่างควบคุมเกม) คลิ๊ก Save เพื่อบันทึกค่า แล้วปิดกรอบไป

กรณีเปิดเกมหรือกรอบโปรแกรมใดๆ ให้คลิ๊กขวาตรงขอบนั้นๆ จะแสดงเมนูการตั้งค่าความโปร่งใส ให้คลิ๊ก No Glass Effect เพื่อยกเลิกการทำงานในกรอบนั้นๆ

หลังจากปรับแต่งแล้ว ให้กลับมาปิดการแสดงคำสั่งเมื่อคลิ๊กขวา Transparency Popup Right Click : Disabled คลิ๊ก save
ขอขอบคุณ
สาคอมพิวเตอร์